V-measure¶
The V-Measure is defined as the harmonic mean of homogeneity 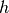 and completeness
and completeness  of the clustering. Both these measures can be expressed in terms of the mutual information and entropy measures of the information theory.
of the clustering. Both these measures can be expressed in terms of the mutual information and entropy measures of the information theory.
Homogeneity 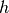 is maximized when each cluster contains elements of as few different classes as possible. Completeness
is maximized when each cluster contains elements of as few different classes as possible. Completeness  aims to put all elements of each class in single clusters.
aims to put all elements of each class in single clusters.
References:
Andrew Rosenberg and Julia Hirschberg, 2007. “V-Measure: A conditional entropy-based external cluster evaluation measure”
The metric is implemented by the vmeasure function:
-
vmeasure(assign1, assign2; β = 1.0)¶ Compute V-measure value between two clustering assignments.
Parameters: - assign1 – the vector of assignments for the first clustering.
- assign2 – the vector of assignments for the second clustering.
- β – the weight of harmonic mean of homogeneity and completeness.
Returns: a V-measure value.
-
vmeasure(R, assign) This method takes
R, an instance ofClusteringResult, and the corresponding assignment vectorassignas input, and computes V-measure value (see above).
-
vmeasure(R1, R2) This method takes
R1andR2(both are instances ofClusteringResult) and computes V-measure value (see above).It is equivalent tovmeasure(assignments(R1), assignments(R1)).